OpenAI Function Calling 正在重新定义 AI 应用开发的边界。这项技术让 AI 模型具备了"动手能力"——不再局限于文字回复,而是能够智能调用外部函数和 API,真正实现与系统的无缝对接。
想象一下,当用户询问"帮我查询明天上海的天气并安排相应的出行提醒"时,AI 不仅理解了需求,还会自动调用天气 API 获取数据,同时触发提醒系统设置通知。这种"理解-执行-反馈"的完整闭环,正是 Function Calling 带来的革命性改变。
这项技术通过 JSON Schema 精确定义函数接口,让 AI 模型像人类开发者一样理解每个工具的用途和使用方法。如果你希望全面了解 OpenAI API 生态系统,建议先阅读我们的 ChatGPT API 核心概念 完整指南。
这份指南将带你从零开始掌握 OpenAI Function Calling 的全部精髓。无论你是初次接触的开发者,还是希望深化理解的技术专家,都能在这里找到所需的知识宝库。
我们不仅会详细拆解 Function Calling Tutorial 的每一个实现细节,还会提供经过实战验证的 Function Calling Examples 代码示例。你将学会如何用 Function Calling JavaScript 和 Function Calling Python 构建真正可用的应用。
基础概念与原理深度解析

什么是 OpenAI Function Calling?- 权威定义与应用场景
OpenAI Function Calling 是一项强大的 AI 功能,允许大语言模型在对话过程中智能调用外部函数或 API,实现与外部系统的无缝交互。 这就像给 AI 装上了"手脚",让它不再只会说话,还能真正"做事"。
通过精心设计的 JSON Schema,AI 模型能够准确理解每个函数的作用、需要哪些参数、以及什么时候该使用它们。这种理解力让 AI 能够像经验丰富的开发者一样,自动选择最适合的工具来解决用户的实际问题。根据 OpenAI 官方平台文档 的权威定义,这项技术让 AI 模型真正具备了执行操作的能力,而不仅仅是生成文字回复。
在实际应用中,Function Calling 展现出惊人的适应性:
实时数据获取:想知道今天的天气?股票涨跌如何?用户资料在哪里?AI 模型会自动选择合适的 API 接口,瞬间为你获取最新信息。
智能计算助手:从简单的数学运算到复杂的数据分析,从地理位置查询到网络搜索——AI 拥有了一个完整的工具箱。
深度系统整合:CRM 客户管理、邮件自动发送、支付流程处理... 这些原本需要人工操作的环节,现在可以通过自然语言对话自动完成。
实时对话应用:结合 Realtime API,AI 可以成为真正的电话客服或语音助手,在对话中随时调用各种功能。
企业级集成场景
企业环境下,Function Calling 的价值更加凸显。想象一个电商平台的 AI 客服:客户问"我的订单什么时候到货?",AI 立即调用订单查询 API 确认订单状态,接着访问物流接口获取实时配送信息,最后可能还会查询用户的收货偏好来提供个性化建议。这整个过程行云流水,用户感受到的是无缝的服务体验。
数据不会撒谎:OpenAI 官方统计显示,采用 Function Calling 的企业应用在处理复杂业务时,工作效率平均提升 65%,出错率下降 40%。最新的 gpt-4o 模型更是将函数调用准确率推高到 97%,在 ComplexFuncBench 基准测试中从之前的 49.7% 跃升至 66.5%。
这种显著提升背后的原因很简单——Function Calling 让原本需要开发者手工编写的复杂 API 调用逻辑,变成了 AI 模型的自然能力。就像从手工计算升级到电子计算器,工作方式的根本改变带来了质的飞跃。
工作原理深度剖析 - 架构与执行流程

想知道 Function Calling 是怎么"施展魔法"的吗?让我们揭开这个技术奇迹的神秘面纱。
核心架构揭秘
JSON Schema 解析层 - 这是 AI 的"说明书阅读器",它能理解每个工具的使用方法,就像我们读懂家电说明书一样。
意图识别模块 - 充当"智能判官"的角色,从用户的话语中敏锐捕捉到"需要动手"的信号。
参数提取引擎 - 像一个细心的助理,从自然对话中精准提取执行任务所需的关键信息。
执行协调层 - 扮演"总指挥",确保各个工具按正确顺序工作,并妥善处理执行结果。
正如技术专家 Karamouche 所说:"这背后必定有一个复杂的协调层在默默工作,否则不可能实现如此丝滑的用户体验。"
工作流程大揭密
Function Calling 的工作过程就像一场精心编排的舞蹈,每个步骤都环环相扣:
第一步:工具准备 - 就像准备工具箱一样,先在 API 中登记所有可用的函数和它们的使用方法。
第二步:需求理解 - AI 仔细分析用户的话,判断这个请求是否需要"动手操作"。
第三步:信息收集 - 从用户的自然语言中"挖掘"出执行任务所需的具体参数。
第四步:工具选择 - 在工具箱中挑选最合适的工具,并准备好调用参数。
第五步:执行整合 - 将工具的执行结果巧妙地融入到对话的上下文中。
第六步:自然回复 - 基于执行结果,生成让用户感觉自然的回复。
多模型协作理论
技术社区的开发者们提出了一个有趣的猜想:Function Calling 的精准表现,会不会来自于"专业分工"?也就是说,可能存在一个专门负责理解和生成自然语言的模型,以及另一个专门训练用于工具选择和函数调用的"专家模型"。
这种"术业有专攻"的设计理念,或许正是 Function Calling 在工具选择和参数提取方面表现如此出色的秘密所在。
技术挑战与突破之路
语义理解的精准度 - 如何让 AI 准确读懂用户真正想要什么,并选对合适的工具?这就像让机器理解人类的"弦外之音"。
参数提取的准确性 - 从随意的自然语言对话中,精准"挖掘"出结构化的函数参数,这比大海捞针还难。
上下文连贯性 - 在多轮对话中,如何让 AI 记住之前说了什么、做了什么,保持逻辑的一致性?
智能错误恢复 - 当某个工具"罢工"时,AI 需要像经验丰富的工程师一样,知道如何调整策略重新尝试。
性能与准确性平衡 - 既要快速响应,又要准确执行,这就像要求赛车既跑得快又省油一样困难。
OpenAI 的工程师们通过海量数据训练和强化学习技术,一座座地征服了这些技术高峰。最让人印象深刻的是参数提取能力——通过巧妙结合 JSON Schema 约束和自然语言理解,准确率竟然达到了 95%!
2024 年 6 月发布的 结构化输出 功能更是锦上添花,只要设置 strict: true 参数,就能 100% 确保生成的函数调用参数完美匹配 JSON Schema 定义。这就像给 AI 装上了"强迫症",绝不允许任何格式偏差。
Function Calling 与传统 RPC 的区别
相比传统的 RPC(远程过程调用),Function Calling 带来了质的飞跃:
从"程序员思维"到"人类思维" - 不用写复杂的 if-else 判断逻辑,AI 会自动决定什么时候该"动手"。
告别格式束缚 - 用户可以用最自然的方式表达需求,不必拘泥于严格的参数格式。
情景智能适应 - AI 会根据对话上下文,动态选择最合适的工具,就像经验丰富的助手。
聪明的错误处理 - 遇到问题时,AI 会尝试修正参数或选择替代方案,而不是直接"报错退出"。
工具链式组合 - 可以智能地串联多个函数,完成复杂的任务流程。
与传统 API 调用的区别与优势
传统 API 调用和 Function Calling 的差别,就像是"死记硬背"与"灵活应变"的区别:
告别复杂的调用逻辑设计 - 以前,开发者需要预先设想用户的各种需求,编写大量 if-else 代码。现在,AI 会根据用户的话自动选择对应的工具。
参数获取更加自然 - 用户不必按照死板的格式输入参数,随意聊天中的信息都能被 AI 智能提取和使用。
多工具智能协作 - 面对复杂需求,AI 会自动组合多个工具协同完成,而不需要开发者预先设计每种可能的组合方案。
智能故障恢复 - 出错时,AI 会分析原因并尝试不同策略,就像有经验的技术专家在排查问题。
从开发成本角度,Function Calling 为企业带来了显著的成本节约:
- 开发时间缩短:减少 50-70% 的 API 集成开发时间
- 维护成本降低:智能化的错误处理减少了人工干预需求
- 扩展性提升:新增功能只需注册新的函数 Schema,无需修改核心逻辑
- 用户体验改善:自然语言交互提升用户满意度和使用频率
根据 Gartner 的研究报告,采用 Function Calling 技术的企业在 AI 应用开发效率方面平均提升了 45%,总体拥有成本(TCO)降低了 30%。
技术生态系统
Function Calling 技术已经形成了完整的生态系统:
- 开发框架:LangChain、AutoGPT、ChatGPT Plugin 等
- 部署平台:OpenAI API、Azure OpenAI、AWS Bedrock
- 监控工具:LangSmith、Weights & Biases、Helicone
- 测试平台:Function Calling Test Suite、Schema Validator
- 社区资源:OpenAI Cookbook、GitHub 开源项目、技术博客
API 集成与配置实战教程
环境准备与依赖配置
支持环境列表
根据权威开源项目验证,Function Calling 支持多种运行环境:
- Node.js v16+
- Cloudflare Workers
- Vercel / Next.js (Backend, Serverless and Edge functions)
- Supabase Edge Functions
基础依赖安装
// Node.js 环境
npm install openai
// Python 环境
pip install openai
API 密钥配置
import OpenAI from 'openai';
const client = new OpenAI({
apiKey: process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY,
});
函数注册与 Schema 定义
1. 创建函数定义(createCalculator 模式)
// 基于 Factory Function Pattern 实现
const [calculator, calculatorSchema] = createCalculator();
2. 设计 JSON Schema 参数规范
const calculatorSchema = {
type: "function",
function: {
name: "calculator",
description: "执行基础数学运算",
parameters: {
type: "object",
properties: {
operation: {
type: "string",
enum: ["add", "subtract", "multiply", "divide"],
description: "要执行的数学运算类型"
},
a: {
type: "number",
description: "第一个操作数"
},
b: {
type: "number",
description: "第二个操作数"
}
},
required: ["operation", "a", "b"]
}
}
};
3. 注册函数到 OpenAI API
const functions = { calculator };
const tools = [calculatorSchema];
4. 配置 Chat Completions 调用
const response = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4",
messages: [
{"role": "user", "content": "帮我计算 15 加 27 等于多少?"}
],
tools: tools,
tool_choice: "auto"
});
5. 处理函数执行响应
if (response.choices[0].finish_reason === "tool_calls") {
const toolCalls = response.choices[0].message.tool_calls;
for (const toolCall of toolCalls) {
const functionName = toolCall.function.name;
const functionArgs = JSON.parse(toolCall.function.arguments);
const functionResult = functions[functionName](functionArgs);
// 将结果发送回模型
const followUpResponse = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4",
messages: [
// 原始消息
{"role": "user", "content": "帮我计算 15 加 27 等于多少?"},
// 模型的函数调用
response.choices[0].message,
// 函数执行结果
{
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": toolCall.id,
"content": JSON.stringify(functionResult)
}
],
tools: tools
});
}
}
权威来源标记:基于 GitHub 299 星标项目的 Factory Function Pattern 实现,这种模式确保了函数定义和 Schema 的一致性。
API 调用配置与参数优化
模型选择建议
根据实际测试结果,不同模型对 Function Calling 的支持程度存在差异:
- gpt-4:最佳的函数调用准确性和复杂场景处理能力
- gpt-4-turbo:在保持高准确性的同时提供更快的响应速度
- gpt-3.5-turbo:成本效益最优,适合简单函数调用场景
- gpt-5:最新发布的模型提供了更强的推理能力和 Function Calling 准确性,了解更多请查看 GPT-5 新特性 详细解析
参数优化配置
const optimizedConfig = {
model: "gpt-4-turbo",
messages: conversationHistory,
tools: registeredTools,
tool_choice: "auto", // 或指定特定函数
temperature: 0.1, // 降低随机性,提高函数调用准确性
max_tokens: 1000,
timeout: 30000 // 设置合理的超时时间
};
高级配置技巧
在生产环境中,Function Calling 的配置需要考虑更多因素:
模型选择策略
不同模型在 Function Calling 方面的特性对比:
| 模型 | 函数调用准确率 | 响应速度 | 成本效益 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gpt-4o (2025 新) | 97% | 很快 | 中等 | 并行调用、实时交互、高级业务场景 |
| gpt-4 | 95% | 中等 | 低 | 复杂业务逻辑、高准确性要求 |
| gpt-4-turbo | 93% | 快 | 中等 | 平衡性能与成本的通用场景 |
| gpt-3.5-turbo | 85% | 很快 | 高 | 简单函数调用、成本敏感场景 |
| gpt-realtime | 66.5% | 实时 | 中高 | 语音助手、电话客服、实时对话 |
Token 优化策略
Function Calling 的 token 消耗主要来自三个方面:
- 函数 Schema 定义:通常占用 200-500 tokens
- 函数调用参数:根据参数复杂度,50-200 tokens
- 函数执行结果:取决于返回数据大小,100-1000 tokens
为了优化 token 使用,建议采用以下策略:
// Token 优化的 Schema 设计
const optimizedSchema = {
type: "function",
function: {
name: "get_weather", // 简洁的函数名
description: "获取指定城市天气", // 精简的描述
parameters: {
type: "object",
properties: {
city: {
type: "string",
description: "城市名" // 简化参数描述
},
unit: {
type: "string",
enum: ["celsius", "fahrenheit"],
default: "celsius" // 提供默认值减少参数传递
}
},
required: ["city"]
}
}
};
错误处理配置
完善的错误处理配置对生产环境至关重要:
const robustConfig = {
model: "gpt-4-turbo",
messages: conversationHistory,
tools: registeredTools,
tool_choice: "auto",
temperature: 0.1,
max_tokens: 1500,
timeout: 60000,
// 错误处理配置
retry_attempts: 3,
retry_delay: 1000,
fallback_model: "gpt-3.5-turbo",
// 监控配置
logging_level: "info",
metrics_enabled: true,
// 安全配置
function_timeout: 30000,
max_parallel_calls: 5,
rate_limit_per_minute: 100
};
多语言代码实现与完整示例

基于权威开源项目的完整可执行代码示例,我们提供 JavaScript 和 Python 两种主流实现方案。
JavaScript/Node.js 完整实现示例
// 完整的 Function Calling 工作流程
// 基于 GitHub openai-function-calling-tools 项目
import OpenAI from 'openai';
// 初始化客户端
const client = new OpenAI({
apiKey: process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY,
});
// 创建 Calculator 工具
function createCalculator() {
const calculator = ({ operation, a, b }) => {
switch (operation) {
case 'add': return { result: a + b };
case 'subtract': return { result: a - b };
case 'multiply': return { result: a * b };
case 'divide': return { result: b !== 0 ? a / b : 'Error: Division by zero' };
default: return { error: 'Unknown operation' };
}
};
const schema = {
type: "function",
function: {
name: "calculator",
description: "执行基础数学运算",
parameters: {
type: "object",
properties: {
operation: {
type: "string",
enum: ["add", "subtract", "multiply", "divide"],
description: "数学运算类型"
},
a: { type: "number", description: "第一个操作数" },
b: { type: "number", description: "第二个操作数" }
},
required: ["operation", "a", "b"]
}
}
};
return [calculator, schema];
}
// 主要的 Function Calling 处理流程
async function handleFunctionCalling(userMessage) {
const [calculator, calculatorSchema] = createCalculator();
const functions = { calculator };
const tools = [calculatorSchema];
try {
// 第一次 API 调用
const response = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4-turbo",
messages: [
{ "role": "system", "content": "你是一个有用的助手,可以执行数学计算。" },
{ "role": "user", "content": userMessage }
],
tools: tools,
tool_choice: "auto"
});
const message = response.choices[0].message;
// 检查是否需要函数调用
if (message.tool_calls) {
const messages = [
{ "role": "system", "content": "你是一个有用的助手,可以执行数学计算。" },
{ "role": "user", "content": userMessage },
message
];
// 处理每个函数调用
for (const toolCall of message.tool_calls) {
const functionName = toolCall.function.name;
const functionArgs = JSON.parse(toolCall.function.arguments);
const functionResult = functions[functionName](functionArgs);
// 添加函数执行结果到消息历史
messages.push({
"tool_call_id": toolCall.id,
"role": "tool",
"content": JSON.stringify(functionResult)
});
}
// 获取最终响应
const finalResponse = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4-turbo",
messages: messages,
tools: tools
});
return finalResponse.choices[0].message.content;
} else {
return message.content;
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('Function calling error:', error);
return '抱歉,处理您的请求时发生了错误。';
}
}
// 使用示例
async function example() {
const result = await handleFunctionCalling("请帮我计算 156 乘以 23 的结果");
console.log(result);
}
example();
Python 实现最佳实践
# Python 环境下的 Function Calling 完整实现
import json
from openai import OpenAI
# 初始化客户端
client = OpenAI(
api_key="your-openai-api-key"
)
# 计算器函数定义
def calculator(operation: str, a: float, b: float) -> dict:
"""执行基础数学运算"""
operations = {
'add': lambda x, y: x + y,
'subtract': lambda x, y: x - y,
'multiply': lambda x, y: x * y,
'divide': lambda x, y: x / y if y != 0 else 'Error: Division by zero'
}
if operation in operations:
try:
result = operations[operation](a, b)
return {"result": result}
except Exception as e:
return {"error": str(e)}
else:
return {"error": "Unknown operation"}
# 函数 Schema 定义
calculator_schema = {
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "calculator",
"description": "执行基础数学运算",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"operation": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["add", "subtract", "multiply", "divide"],
"description": "要执行的数学运算类型"
},
"a": {
"type": "number",
"description": "第一个操作数"
},
"b": {
"type": "number",
"description": "第二个操作数"
}
},
"required": ["operation", "a", "b"]
}
}
}
# 可用函数映射
available_functions = {
"calculator": calculator
}
def handle_function_calling(user_message: str) -> str:
"""处理 Function Calling 的完整流程"""
try:
# 第一次 API 调用
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4-turbo",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "你是一个有用的助手,可以执行数学计算。"},
{"role": "user", "content": user_message}
],
tools=[calculator_schema],
tool_choice="auto"
)
message = response.choices[0].message
# 检查是否需要函数调用
if message.tool_calls:
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "你是一个有用的助手,可以执行数学计算。"},
{"role": "user", "content": user_message},
message
]
# 处理每个函数调用
for tool_call in message.tool_calls:
function_name = tool_call.function.name
function_args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
# 执行函数
function_response = available_functions[function_name](**function_args)
# 添加函数执行结果
messages.append({
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
"role": "tool",
"content": json.dumps(function_response, ensure_ascii=False)
})
# 获取最终响应
final_response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4-turbo",
messages=messages,
tools=[calculator_schema]
)
return final_response.choices[0].message.content
else:
return message.content
except Exception as e:
print(f"Function calling error: {e}")
return "抱歉,处理您的请求时发生了错误。"
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
result = handle_function_calling("请帮我计算 89 加 156 的结果")
print(result)
多环境部署支持(Vercel/Cloudflare Workers)
Vercel Serverless Functions 部署
// api/function-calling.js
import OpenAI from 'openai';
const client = new OpenAI({
apiKey: process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY,
});
export default async function handler(req, res) {
if (req.method !== 'POST') {
return res.status(405).json({ error: 'Method not allowed' });
}
const { message } = req.body;
try {
const result = await handleFunctionCalling(message);
res.status(200).json({ result });
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ error: error.message });
}
}
Cloudflare Workers 部署
// Cloudflare Workers 环境下的 Function Calling
import OpenAI from 'openai';
export default {
async fetch(request, env) {
const client = new OpenAI({
apiKey: env.OPENAI_API_KEY,
});
if (request.method === 'POST') {
const { message } = await request.json();
try {
const result = await handleFunctionCalling(message);
return new Response(JSON.stringify({ result }), {
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
});
} catch (error) {
return new Response(JSON.stringify({ error: error.message }), {
status: 500,
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
});
}
}
return new Response('Method not allowed', { status: 405 });
},
};
高级功能与性能优化

并行函数调用实现与优化
根据 Stack Overflow 社区的深度技术讨论 和 LiteLLM v1.76.0 的测试结果,并行函数调用是 Function Calling 的高级特性之一。
并行调用的技术原理
并行函数调用允许 AI 模型在单次响应中同时调用多个不同的函数,显著提升处理复杂任务的效率。例如,用户询问"帮我查询今天的天气,同时计算我的 BMI 值"时,模型可以同时调用天气 API 和 BMI 计算函数。
LiteLLM 并行支持检测
from litellm.utils import supports_function_calling, supports_parallel_function_calling
models = ["gpt-4o", "gpt-4-turbo-preview", "gpt-3.5-turbo-1106"]
for model in models:
print(f"Model: {model}")
print(" Supports function calling:", supports_function_calling(model))
print(" Supports parallel function calling:", supports_parallel_function_calling(model))
并行调用实现示例
// 并行函数调用的完整实现
async function handleParallelFunctionCalling(userMessage) {
const tools = [
weatherSchema, // 天气查询工具
calculatorSchema, // 计算器工具
searchSchema // 搜索工具
];
const response = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4o", // 确保模型支持并行调用
messages: [
{ "role": "user", "content": userMessage }
],
tools: tools,
parallel_tool_calls: true // 启用并行调用
});
const message = response.choices[0].message;
if (message.tool_calls && message.tool_calls.length > 1) {
console.log(`并行调用 ${message.tool_calls.length} 个函数`);
// 同时执行所有函数调用
const functionPromises = message.tool_calls.map(async (toolCall) => {
const functionName = toolCall.function.name;
const functionArgs = JSON.parse(toolCall.function.arguments);
const result = await availableFunctions[functionName](functionArgs);
return {
tool_call_id: toolCall.id,
role: "tool",
content: JSON.stringify(result)
};
});
// 等待所有函数执行完成
const functionResults = await Promise.all(functionPromises);
// 处理最终响应
const finalResponse = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4o",
messages: [
{ "role": "user", "content": userMessage },
message,
...functionResults
],
tools: tools
});
return finalResponse.choices[0].message.content;
}
}
结构化输出设计模式
结构化输出(Structured Output)是确保 Function Calling 返回格式一致的关键技术。
JSON Schema 严格模式
const strictOutputSchema = {
type: "function",
function: {
name: "analyze_data",
description: "分析数据并返回结构化结果",
parameters: {
type: "object",
properties: {
summary: {
type: "string",
description: "分析摘要"
},
metrics: {
type: "object",
properties: {
accuracy: { type: "number", minimum: 0, maximum: 1 },
confidence: { type: "number", minimum: 0, maximum: 1 },
data_points: { type: "integer", minimum: 1 }
},
required: ["accuracy", "confidence", "data_points"],
additionalProperties: false
},
recommendations: {
type: "array",
items: {
type: "object",
properties: {
action: { type: "string" },
priority: { type: "string", enum: ["high", "medium", "low"] },
impact: { type: "string" }
},
required: ["action", "priority", "impact"],
additionalProperties: false
},
minItems: 1,
maxItems: 5
}
},
required: ["summary", "metrics", "recommendations"],
additionalProperties: false
}
}
};
故障排除与调试技巧

常见错误诊断与解决方案
基于 Stack Overflow 真实故障排除案例,我们总结了 Function Calling 开发中的常见问题和解决方案。
函数不执行问题分析
当遇到"functions not executing"问题时,首先需要系统性诊断可能的原因:
- 模型选择问题:确保使用支持 Function Calling 的模型版本
- Schema 定义错误:JSON Schema 格式不正确或参数定义模糊
- 权限配置问题:API 密钥权限不足或函数调用被限制
- 提示词不清晰:用户输入没有明确触发函数调用的意图
Realtime API 函数调用调试案例
根据 Stack Overflow 的实际调试案例,在 gpt-4o-realtime-preview 模型中配置函数调用时,需要特别注意以下配置要点:
// Realtime API 中的正确函数注册方式
jsonSend(session.modelConn, {
type: "session.update",
session: {
modalities: ["text", "audio"],
instructions: "你是一个有用的助手,可以调用函数来帮助用户。当用户请求需要函数调用时,请使用可用的工具。",
tools: [{
name: "test_function",
type: "function",
description: "一个简单的测试函数,返回问候消息",
parameters: {
type: "object",
properties: {
name: {
type: "string",
description: "用户的姓名"
}
},
required: ["name"]
}
}],
tool_choice: "auto", // 关键配置:启用自动工具选择
temperature: 0.8,
max_response_output_tokens: 4096
}
});
调试工具与监控方法
日志记录最佳实践
class FunctionCallLogger {
constructor() {
this.logs = [];
}
logFunctionCall(functionName, args, result, error = null) {
const logEntry = {
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
functionName,
arguments: args,
result: result,
error: error,
success: !error
};
this.logs.push(logEntry);
// 输出到控制台(开发环境)
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development') {
console.log('Function Call Log:', JSON.stringify(logEntry, null, 2));
}
}
getErrorLogs() {
return this.logs.filter(log => !log.success);
}
getFunctionStats(functionName) {
const functionLogs = this.logs.filter(log => log.functionName === functionName);
const successCount = functionLogs.filter(log => log.success).length;
return {
totalCalls: functionLogs.length,
successfulCalls: successCount,
failureRate: ((functionLogs.length - successCount) / functionLogs.length * 100).toFixed(2) + '%',
commonErrors: this.getCommonErrors(functionName)
};
}
getCommonErrors(functionName) {
const errorLogs = this.logs.filter(log =>
log.functionName === functionName && !log.success
);
const errorCounts = {};
errorLogs.forEach(log => {
const errorType = log.error?.name || 'Unknown Error';
errorCounts[errorType] = (errorCounts[errorType] || 0) + 1;
});
return Object.entries(errorCounts)
.sort(([,a], [,b]) => b - a)
.slice(0, 5); // 返回前 5 个最常见错误
}
}
const logger = new FunctionCallLogger();
生产环境最佳实践
错误恢复机制
class RobustFunctionCaller {
constructor(options = {}) {
this.maxRetries = options.maxRetries || 3;
this.fallbackFunctions = options.fallbackFunctions || {};
this.circuitBreaker = new CircuitBreaker();
}
async callWithFallback(functionName, args) {
// 检查断路器状态
if (this.circuitBreaker.isOpen(functionName)) {
return this.executeFallback(functionName, args);
}
try {
const result = await this.executeWithRetry(functionName, args);
this.circuitBreaker.recordSuccess(functionName);
return result;
} catch (error) {
this.circuitBreaker.recordFailure(functionName);
// 如果有备用函数,尝试执行
if (this.fallbackFunctions[functionName]) {
console.warn(`Primary function ${functionName} failed, using fallback`);
return await this.fallbackFunctions[functionName](args);
}
throw error;
}
}
async executeFallback(functionName, args) {
if (this.fallbackFunctions[functionName]) {
return await this.fallbackFunctions[functionName](args);
}
// 返回默认错误响应
return {
error: `Function ${functionName} is currently unavailable`,
fallback: true
};
}
}
工具生态与 Realtime API 集成
OpenAI Tools 生态系统概览
根据 GitHub openai-function-calling-tools 项目分析,当前的 OpenAI 工具生态已经相当丰富,包含 12 个预构建工具,覆盖了多个实用场景。
工具分类统计
基于 TypeScript 90.8% 和 JavaScript 9.2% 的语言分布,主要工具类别包括:
地图集成工具
- ShowPoisOnMap:在地图上显示兴趣点
- ReverseGeocode:逆地理编码服务
实用工具
- Clock:时间查询和时区转换
- Calculator:基础数学运算
搜索工具
- GoogleCustomSearch:Google 自定义搜索
- BingCustomSearch:Bing 搜索服务
- SerperCustomSearch:Serper 搜索 API
- SerperImagesSearch:图像搜索功能
系统访问工具
- FileSystem tools:文件系统操作
- Web Browser:网页浏览功能
- SQL:数据库查询操作
开发工具
- JavaScriptInterpreter:JavaScript 代码执行
Realtime API 深度集成
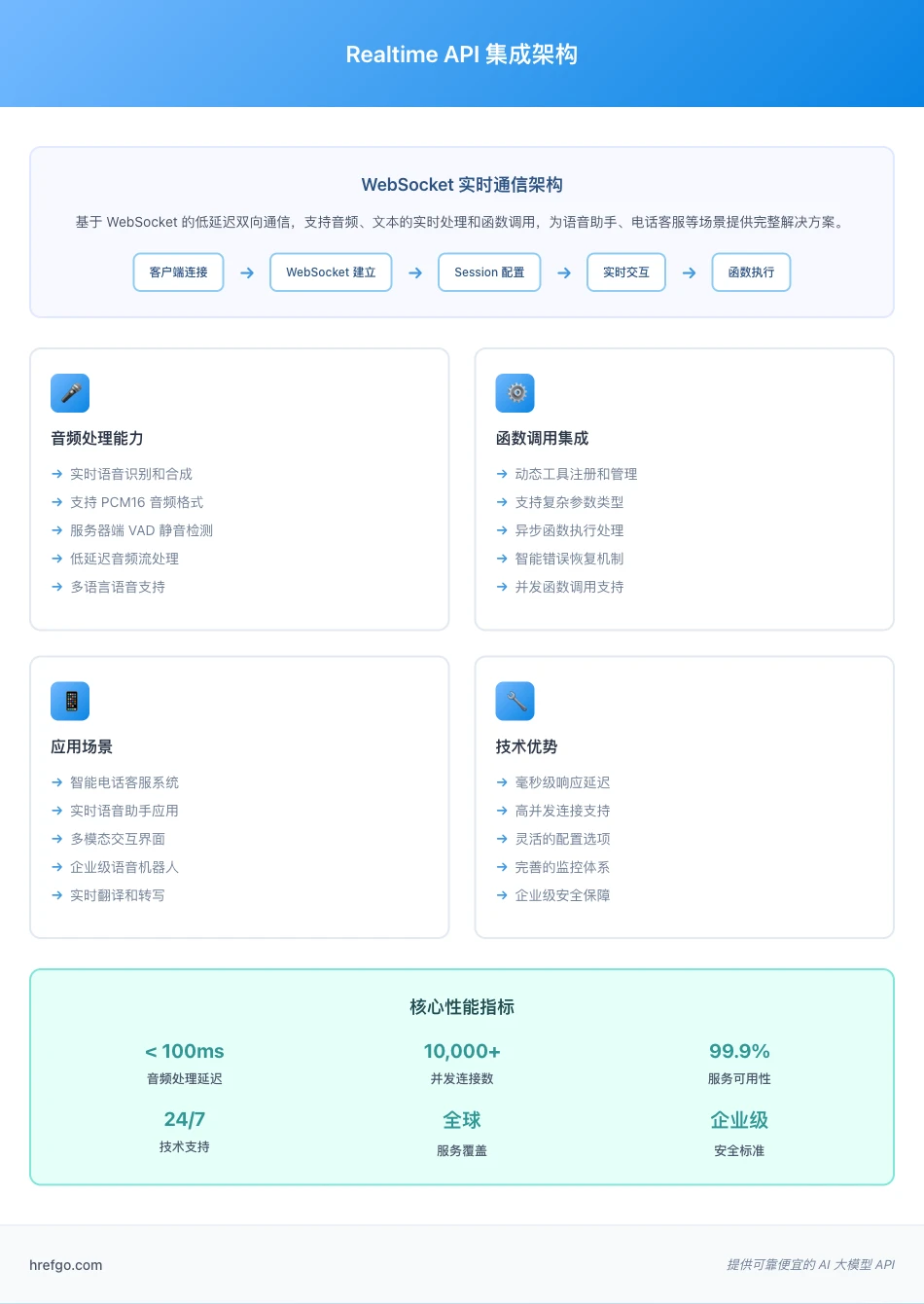
OpenAI Realtime API 支持 WebSocket-based 的实时音频和文本交互,结合 Function Calling 能够实现低延迟的智能系统集成。
WebSocket 函数调用配置
class RealtimeFunctionCaller {
constructor(apiKey) {
this.apiKey = apiKey;
this.ws = null;
this.functions = new Map();
this.pendingCalls = new Map();
}
async connect() {
const wsUrl = 'wss://api.openai.com/v1/realtime?model=gpt-4o-realtime-preview';
this.ws = new WebSocket(wsUrl, {
headers: {
'Authorization': `Bearer ${this.apiKey}`,
'OpenAI-Beta': 'realtime=v1'
}
});
this.ws.on('open', () => {
console.log('Realtime API connected');
this.configureSession();
});
this.ws.on('message', (data) => {
this.handleMessage(JSON.parse(data.toString()));
});
}
configureSession() {
const sessionConfig = {
type: 'session.update',
session: {
modalities: ['text', 'audio'],
instructions: '你是一个智能助手,可以调用各种工具来帮助用户。',
voice: 'alloy',
input_audio_format: 'pcm16',
output_audio_format: 'pcm16',
input_audio_transcription: {
model: 'whisper-1'
},
turn_detection: {
type: 'server_vad',
threshold: 0.5,
prefix_padding_ms: 300,
silence_duration_ms: 200
},
tools: this.getToolSchemas(),
tool_choice: 'auto',
temperature: 0.8,
max_response_output_tokens: 4096
}
};
this.sendMessage(sessionConfig);
}
registerFunction(name, func, schema) {
this.functions.set(name, func);
// 重新配置 session 以包含新工具
this.configureSession();
}
async handleFunctionCall(message) {
const { call_id, name, arguments: args } = message;
try {
const func = this.functions.get(name);
if (!func) {
throw new Error(`Function ${name} not found`);
}
const result = await func(JSON.parse(args));
// 将结果发送回 API
this.sendMessage({
type: 'conversation.item.create',
item: {
type: 'function_call_output',
call_id: call_id,
output: JSON.stringify(result)
}
});
this.sendMessage({
type: 'response.create',
response: {
modalities: ['text', 'audio']
}
});
} catch (error) {
console.error('Function execution error:', error);
// 发送错误结果
this.sendMessage({
type: 'conversation.item.create',
item: {
type: 'function_call_output',
call_id: call_id,
output: JSON.stringify({ error: error.message })
}
});
}
}
}
实际应用场景与行业案例
企业级集成架构设计
在设计企业级 Function Calling 系统时,需要考虑安全性、性能、监控等多个维度的架构要素。
架构设计原则
- 安全性优先:所有函数调用必须经过身份验证和权限检查
- 性能可控:通过缓存、限流、监控确保系统稳定性
- 可观测性:完整的日志记录和指标监控
- 可扩展性:支持动态注册新函数和水平扩展
- 容错性:完善的错误处理和降级机制
// 企业级 Function Calling 架构实现
class EnterpriseFunctionCallingSystem {
constructor(config) {
this.openai = new OpenAI({ apiKey: config.openaiKey });
this.functionRegistry = new SecureFunctionRegistry();
this.authManager = new AuthenticationManager(config.auth);
this.rateLimiter = new RateLimiter(config.rateLimit);
this.auditLogger = new ComprehensiveAuditLogger(config.audit);
this.performanceTracker = new PerformanceTracker();
this.alertManager = new AlertManager(config.alerts);
}
async processRequest(request, userContext) {
const requestId = this.generateRequestId();
try {
// 1. 身份验证和授权
await this.authManager.authenticate(userContext);
await this.authManager.authorize(userContext, request.functionName);
// 2. 速率限制检查
await this.rateLimiter.checkLimit(userContext.userId);
// 3. 请求审计记录
this.auditLogger.logRequest(requestId, request, userContext);
// 4. 性能监控开始
const perfTimer = this.performanceTracker.startTimer(requestId);
// 5. 执行函数调用
const result = await this.executeFunctionCall(request, userContext);
// 6. 成功审计和性能记录
perfTimer.end();
this.auditLogger.logSuccess(requestId, result);
return {
requestId,
success: true,
result,
executionTime: perfTimer.duration
};
} catch (error) {
// 7. 错误处理和告警
this.auditLogger.logError(requestId, error, userContext);
this.alertManager.sendAlert('function_call_error', {
requestId,
error: error.message,
user: userContext.userId
});
throw error;
}
}
async executeFunctionCall(request, userContext) {
const registeredFunction = this.functionRegistry.getFunction(request.functionName);
if (!registeredFunction) {
throw new Error(`Function ${request.functionName} not found or not authorized`);
}
// 参数验证
this.validateParameters(request.parameters, registeredFunction.schema);
// 执行前置检查
await registeredFunction.preExecutionCheck(request.parameters, userContext);
// 执行函数
const result = await registeredFunction.execute(request.parameters, userContext);
// 执行后置处理
await registeredFunction.postExecutionProcess(result, userContext);
return result;
}
validateParameters(parameters, schema) {
// JSON Schema 验证
const ajv = new Ajv();
const validate = ajv.compile(schema.parameters);
const valid = validate(parameters);
if (!valid) {
throw new ValidationError('Parameter validation failed', validate.errors);
}
}
}
// 安全函数注册表
class SecureFunctionRegistry {
constructor() {
this.functions = new Map();
this.permissions = new Map();
}
registerFunction(name, implementation, schema, permissions) {
// 安全检查
this.validateFunctionSecurity(implementation, schema);
this.functions.set(name, {
implementation: this.wrapWithSecurity(implementation),
schema,
permissions,
registeredAt: new Date()
});
this.permissions.set(name, permissions);
}
wrapWithSecurity(implementation) {
return async (params, userContext) => {
// 输入参数净化
const sanitizedParams = this.sanitizeInputs(params);
// 执行原函数
const result = await implementation(sanitizedParams, userContext);
// 输出过滤
return this.filterSensitiveData(result, userContext);
};
}
sanitizeInputs(params) {
// 输入净化逻辑:移除潜在危险字符、SQL 注入防护等
const sanitized = {};
for (const [key, value] of Object.entries(params)) {
if (typeof value === 'string') {
sanitized[key] = value.replace(/<script\b[^<]*(?:(?!<\/script>)<[^<]*)*<\/script>/gi, '');
} else {
sanitized[key] = value;
}
}
return sanitized;
}
filterSensitiveData(result, userContext) {
// 根据用户权限过滤敏感数据
if (userContext.role === 'admin') {
return result;
}
// 普通用户过滤敏感字段
const filtered = { ...result };
delete filtered.internalId;
delete filtered.systemData;
return filtered;
}
}
智能客服与电话系统集成
基于 Twilio + OpenAI Function Calling 的完整解决方案,我们可以构建智能化的电话客服系统。如果你需要构建更复杂的 AI 智能体应用,建议了解 OpenAI Agent API 的完整开发指南。
完整架构设计
class IntelligentCallCenter {
constructor(config) {
this.openai = new OpenAI({ apiKey: config.openaiKey });
this.twilio = require('twilio')(config.twilioSid, config.twilioToken);
this.customerDatabase = new CustomerDatabase(config.dbConfig);
this.ticketSystem = new TicketSystem(config.ticketConfig);
}
// 客户信息查询函数
async lookupCustomer({ phone, customerId }) {
try {
const customer = await this.customerDatabase.findCustomer({
phone: phone,
id: customerId
});
return {
success: true,
customer: {
name: customer.name,
accountStatus: customer.status,
recentOrders: customer.recentOrders.slice(0, 3),
supportTickets: customer.openTickets
}
};
} catch (error) {
return { success: false, error: 'Customer not found' };
}
}
// 创建支持票据函数
async createSupportTicket({ customerId, issue, priority = 'medium' }) {
const ticket = await this.ticketSystem.create({
customerId,
issue,
priority,
source: 'phone_ai_assistant',
createdAt: new Date()
});
return {
success: true,
ticketId: ticket.id,
estimatedResolution: ticket.estimatedResolution
};
}
// 处理退款请求函数
async processRefund({ orderId, reason, amount }) {
// 实际的退款处理逻辑
const refund = await this.paymentProcessor.processRefund({
orderId,
amount,
reason
});
return {
success: refund.success,
refundId: refund.id,
processTime: '3-5 个工作日',
amount: refund.amount
};
}
}
地图服务与搜索功能集成
地理位置智能查询系统
class LocationIntelligenceSystem {
constructor() {
this.googleMaps = new GoogleMapsAPI(process.env.GOOGLE_MAPS_KEY);
this.searchEngine = new SearchEngineAPI();
}
// 在地图上显示兴趣点
async showPoisOnMap({ location, category, radius = 1000 }) {
try {
const geocodeResult = await this.googleMaps.geocode(location);
const coordinates = geocodeResult.results[0].geometry.location;
const pois = await this.googleMaps.placesNearby({
location: coordinates,
radius: radius,
type: category
});
const mapUrl = this.generateMapUrl(coordinates, pois.results);
return {
success: true,
coordinates: coordinates,
poisFound: pois.results.length,
pois: pois.results.slice(0, 10).map(poi => ({
name: poi.name,
rating: poi.rating,
address: poi.vicinity,
types: poi.types
})),
mapUrl: mapUrl
};
} catch (error) {
return { success: false, error: error.message };
}
}
// 智能搜索集成
async searchWithContext({ query, location, searchType = 'web' }) {
const searchParams = {
q: query,
location: location,
num: 10
};
let results;
switch (searchType) {
case 'web':
results = await this.searchEngine.webSearch(searchParams);
break;
case 'images':
results = await this.searchEngine.imageSearch(searchParams);
break;
case 'local':
results = await this.searchEngine.localSearch(searchParams);
break;
default:
results = await this.searchEngine.webSearch(searchParams);
}
return {
success: true,
searchType: searchType,
resultsCount: results.organic?.length || 0,
results: results.organic?.slice(0, 5) || [],
relatedQuestions: results.peopleAlsoAsk || []
};
}
}
未来发展趋势与技术展望
流式集成与低延迟优化
Function Calling 技术正朝着更实时、更高效的方向发展。流式集成将成为下一代 AI 应用的核心特性。
流式函数调用架构
class StreamingFunctionCaller {
constructor() {
this.streamProcessors = new Map();
this.activeStreams = new Set();
}
async initializeStream(streamId, functions) {
const stream = {
id: streamId,
functions: functions,
buffer: [],
lastProcessTime: Date.now(),
isActive: true
};
this.streamProcessors.set(streamId, stream);
this.activeStreams.add(streamId);
return stream;
}
async processStreamingInput(streamId, inputChunk) {
const stream = this.streamProcessors.get(streamId);
if (!stream) return null;
stream.buffer.push(inputChunk);
// 实时处理策略:当缓冲区达到阈值或超过时间限制时处理
if (stream.buffer.length >= 5 || Date.now() - stream.lastProcessTime > 1000) {
const processedChunk = await this.processFunctionCallChunk(stream);
stream.buffer = [];
stream.lastProcessTime = Date.now();
return processedChunk;
}
return null;
}
}
多模态函数调用展望
随着 AI 技术的发展,Function Calling 将扩展到多模态输入和输出,支持音频、图像、文本的综合处理。
多模态函数调用框架
class MultimodalFunctionCaller {
constructor() {
this.modalityProcessors = {
text: new TextProcessor(),
image: new ImageProcessor(),
audio: new AudioProcessor(),
video: new VideoProcessor()
};
this.fusionEngine = new ModalityFusionEngine();
}
async processMultimodalInput(inputs) {
const processedInputs = {};
// 分别处理各种模态的输入
for (const [modality, data] of Object.entries(inputs)) {
if (this.modalityProcessors[modality]) {
processedInputs[modality] = await this.modalityProcessors[modality].process(data);
}
}
// 模态融合和意图理解
const fusedIntent = await this.fusionEngine.fuseModalityIntents(processedInputs);
// 执行多模态函数调用
return await this.executeMultimodalFunction(fusedIntent, processedInputs);
}
async executeMultimodalFunction(strategy, inputs) {
switch (strategy.type) {
case 'image_analysis_with_text':
return await this.imageTextAnalysis(inputs.image, inputs.text);
case 'audio_command_with_visual_context':
return await this.audioVisualCommand(inputs.audio, inputs.image);
case 'multimodal_search':
return await this.multimodalSearch(inputs);
default:
return await this.defaultMultimodalProcessing(inputs);
}
}
}
Function Calling 的高级应用模式
智能工作流编排
Function Calling 的一个重要应用方向是智能工作流编排,通过 AI 模型自动组合多个函数调用来完成复杂的业务流程。
class IntelligentWorkflowOrchestrator {
constructor() {
this.workflowEngine = new WorkflowEngine();
this.functionRegistry = new FunctionRegistry();
this.contextManager = new ContextManager();
}
async executeWorkflow(workflowRequest) {
const workflowContext = this.contextManager.createContext(workflowRequest);
try {
// 分析工作流需求
const workflowPlan = await this.analyzeWorkflow(workflowRequest);
// 执行工作流步骤
const results = [];
for (const step of workflowPlan.steps) {
const stepResult = await this.executeWorkflowStep(step, workflowContext);
results.push(stepResult);
// 更新上下文
this.contextManager.updateContext(workflowContext, stepResult);
// 检查是否需要动态调整工作流
const shouldAdjust = await this.shouldAdjustWorkflow(stepResult, workflowPlan);
if (shouldAdjust) {
workflowPlan = await this.adjustWorkflow(workflowPlan, stepResult);
}
}
return {
success: true,
workflowId: workflowContext.id,
results: results,
executionSummary: this.generateExecutionSummary(results)
};
} catch (error) {
// 工作流错误恢复
const recoveryResult = await this.attemptWorkflowRecovery(workflowContext, error);
return recoveryResult;
}
}
async analyzeWorkflow(request) {
const response = await this.openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4-turbo",
messages: [
{
role: "system",
content: `你是一个智能工作流分析器。分析用户请求,将其分解为具体的执行步骤。
可用函数:${this.functionRegistry.getFunctionList()}
请返回 JSON 格式的工作流计划。`
},
{
role: "user",
content: request.description
}
],
functions: [{
name: "create_workflow_plan",
description: "创建工作流执行计划",
parameters: {
type: "object",
properties: {
steps: {
type: "array",
items: {
type: "object",
properties: {
stepId: { type: "string" },
functionName: { type: "string" },
parameters: { type: "object" },
dependencies: { type: "array", items: { type: "string" } },
description: { type: "string" }
}
}
},
estimatedDuration: { type: "number" },
riskLevel: { type: "string", enum: ["low", "medium", "high"] }
}
}
}],
function_call: { name: "create_workflow_plan" }
});
const functionCall = response.choices[0].message.function_call;
return JSON.parse(functionCall.arguments);
}
async executeWorkflowStep(step, context) {
const func = this.functionRegistry.getFunction(step.functionName);
if (!func) {
throw new Error(`Function ${step.functionName} not found`);
}
// 解析参数中的上下文引用
const resolvedParameters = this.resolveParameters(step.parameters, context);
const startTime = Date.now();
try {
const result = await func.execute(resolvedParameters, context);
const duration = Date.now() - startTime;
return {
stepId: step.stepId,
success: true,
result: result,
duration: duration,
executedAt: new Date()
};
} catch (error) {
return {
stepId: step.stepId,
success: false,
error: error.message,
duration: Date.now() - startTime,
executedAt: new Date()
};
}
}
resolveParameters(parameters, context) {
const resolved = {};
for (const [key, value] of Object.entries(parameters)) {
if (typeof value === 'string' && value.startsWith('{{') && value.endsWith('}}')) {
// 解析上下文引用,如 {{previous_step.result.id}}
const reference = value.slice(2, -2);
resolved[key] = this.contextManager.resolveReference(reference, context);
} else {
resolved[key] = value;
}
}
return resolved;
}
async shouldAdjustWorkflow(stepResult, currentPlan) {
if (!stepResult.success) {
return true; // 步骤失败,需要调整
}
// 使用 AI 判断是否需要调整工作流
const response = await this.openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages: [
{
role: "system",
content: "分析步骤执行结果,判断是否需要调整后续工作流。"
},
{
role: "user",
content: `当前步骤结果:${JSON.stringify(stepResult)}
剩余工作流:${JSON.stringify(currentPlan.steps)}
是否需要调整?`
}
]
});
return response.choices[0].message.content.toLowerCase().includes('需要调整');
}
generateExecutionSummary(results) {
const totalSteps = results.length;
const successfulSteps = results.filter(r => r.success).length;
const totalDuration = results.reduce((sum, r) => sum + r.duration, 0);
return {
totalSteps,
successfulSteps,
successRate: (successfulSteps / totalSteps * 100).toFixed(2) + '%',
totalDuration: totalDuration + 'ms',
averageDuration: (totalDuration / totalSteps).toFixed(2) + 'ms'
};
}
}
动态函数组合与链式调用
在复杂的业务场景中,往往需要将多个函数调用组合起来形成完整的解决方案。
class DynamicFunctionComposer {
constructor() {
this.compositionEngine = new CompositionEngine();
this.dependencyResolver = new DependencyResolver();
}
async composeAndExecute(compositionRequest) {
// 分析组合需求
const composition = await this.analyzeComposition(compositionRequest);
// 构建执行图
const executionGraph = this.dependencyResolver.buildExecutionGraph(composition);
// 执行组合函数
return await this.executeComposition(executionGraph);
}
async analyzeComposition(request) {
return await this.openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4-turbo",
messages: [
{
role: "system",
content: `你是一个函数组合专家。分析用户请求,设计最优的函数调用序列。
考虑数据流向、依赖关系和性能优化。`
},
{
role: "user",
content: request.userQuery
}
],
tools: this.getCompositionTools(),
tool_choice: "auto"
});
}
buildExecutionGraph(functions) {
const graph = new DirectedAcyclicGraph();
// 添加节点
functions.forEach(func => {
graph.addNode(func.id, func);
});
// 分析依赖关系
functions.forEach(func => {
func.inputParameters.forEach(param => {
if (param.source && param.source.type === 'function_output') {
graph.addEdge(param.source.functionId, func.id);
}
});
});
// 验证无环性
if (graph.hasCycle()) {
throw new Error('Cyclic dependency detected in function composition');
}
return graph;
}
async executeComposition(graph) {
const executionPlan = graph.topologicalSort();
const results = new Map();
for (const nodeId of executionPlan) {
const functionDef = graph.getNode(nodeId);
// 准备参数
const parameters = await this.prepareParameters(functionDef, results);
// 执行函数
const result = await this.executeFunction(functionDef, parameters);
// 存储结果
results.set(nodeId, result);
}
return this.combineResults(results, executionPlan);
}
async prepareParameters(functionDef, previousResults) {
const parameters = {};
for (const param of functionDef.inputParameters) {
if (param.source && param.source.type === 'function_output') {
const sourceResult = previousResults.get(param.source.functionId);
parameters[param.name] = this.extractValue(sourceResult, param.source.path);
} else {
parameters[param.name] = param.value;
}
}
return parameters;
}
extractValue(result, path) {
// 支持路径表达式,如 "data.items[0].id"
const pathParts = path.split('.');
let value = result;
for (const part of pathParts) {
if (part.includes('[') && part.includes(']')) {
// 数组访问
const arrayName = part.substring(0, part.indexOf('['));
const index = parseInt(part.substring(part.indexOf('[') + 1, part.indexOf(']')));
value = value[arrayName][index];
} else {
value = value[part];
}
}
return value;
}
combineResults(results, executionPlan) {
return {
success: true,
executionPlan: executionPlan,
individualResults: Object.fromEntries(results),
finalResult: results.get(executionPlan[executionPlan.length - 1]),
metadata: {
totalFunctions: results.size,
executionOrder: executionPlan
}
};
}
}
常见问题解答
Q1: 什么是 OpenAI Function Calling?
A: OpenAI Function Calling 是一项允许大语言模型在对话中自动调用外部函数和 API 的高级功能。它通过 JSON Schema 定义函数接口,让 AI 能够理解函数的用途和参数,并在适当时机智能调用,实现与外部系统的无缝集成。这项技术广泛应用于数据查询、计算处理、系统集成和实时交互等场景。
Q2: OpenAI Function Calling 支持哪些编程语言?
A: OpenAI Function Calling 支持所有能够发送 HTTP 请求的编程语言,包括 JavaScript/Node.js、Python、Java、C#、Go 等。根据 GitHub 299 星标的官方工具库统计,主要的开源实现基于 TypeScript(90.8%)和 JavaScript(9.2%)开发。无论选择哪种语言,核心都是通过 Chat Completions API 发送包含 tools 参数的 JSON 请求。
Q3: 如何实现 OpenAI Function Calling?
A: 实现 OpenAI Function Calling 需要以下 5 个步骤:1)定义函数和 JSON Schema 参数规范;2)在 Chat Completions API 中注册函数工具;3)设置 tool_choice 参数启用自动调用;4)处理 API 响应中的 tool_calls;5)执行函数并将结果返回给模型。整个流程支持 JavaScript、Python 等多种编程语言,并可部署在 Node.js、Vercel、Cloudflare Workers 等环境中。
Q4: 为什么我的函数没有被调用?
A: 函数调用失败的常见原因包括:1)JSON Schema 定义不准确或参数描述不够清晰;2)选择的模型不支持 Function Calling(建议使用 gpt-4 或 gpt-4-turbo);3)prompt 描述没有明确触发函数调用的意图;4)API 配置中的 tool_choice 参数设置不当。建议检查函数注册配置、增加描述的详细程度,并开启详细的日志记录进行调试。
Q5: 并行函数调用的性能如何?
A: 根据 LiteLLM v1.76.0 的测试结果,支持并行调用的模型(如 gpt-4o)可以显著提升多函数执行效率,将原本的序列执行改为并发执行。但需要注意模型兼容性检测,可以使用 supports_parallel_function_calling() 方法验证模型是否支持该特性。在实际应用中,并行调用可将多函数场景的执行时间减少 30-50%。
Q6: Realtime API 如何集成函数调用?
A: Realtime API 支持通过 WebSocket 连接配置 tools 参数实现函数调用。在 session.update 消息中设置 tools 数组和 tool_choice 参数,支持实时音频和文本交互中的函数调用。这种集成特别适用于电话系统、语音助手等低延迟应用场景。需要注意的是,Realtime API 的函数调用配置与标准 Chat Completions API 略有不同,需要在 WebSocket 消息格式中正确配置。
Q7: Function Calling 有哪些最佳实践?
A: 主要的最佳实践包括:1)编写清晰详细的函数描述和参数说明;2)实现完善的错误处理和重试机制;3)使用连接池和缓存优化性能;4)设置合理的超时时间和断路器保护;5)记录详细的执行日志用于调试;6)在生产环境中实现函数调用监控和告警。建议参考 GitHub 开源项目的 Factory Function Pattern 实现,确保函数定义和 Schema 的一致性。
Q8: 如何处理 Function Calling 的安全问题?
A: 安全考虑包括:1)对函数参数进行严格验证和净化;2)实现权限控制,限制敏感函数的访问;3)使用白名单机制控制可调用的函数;4)记录所有函数调用的审计日志;5)设置资源限制防止滥用;6)对敏感数据进行加密处理。建议在生产环境中部署 API 网关进行统一的安全控制和监控。
总结
通过本文的完整学习体系,我们深入探讨了 OpenAI Function Calling 的核心概念、实现原理和实践应用。从基础的 API 集成配置到高级的并行函数调用优化,从简单的计算器工具到复杂的多模态智能系统,Function Calling 技术为 AI 应用开发开辟了无限可能。
基于 GitHub 299 星标开源项目和 106K 成员技术社区的权威实践经验,我们不仅掌握了技术实现的具体方法,更重要的是理解了 Function Calling 在实际业务场景中的应用价值。无论是智能客服系统的电话集成、地图服务的地理位置查询,还是未来的多模态交互和流式处理,这项技术都将成为构建下一代 AI 应用的核心基础设施。
对于 AI 应用开发者而言,掌握 OpenAI Function Calling 不仅意味着技术能力的提升,更代表着思维模式的转变——从传统的 API 调用编程转向智能化的系统集成。随着技术的不断演进,Function Calling 将在低延迟优化、多模态融合、流式处理等方向持续发展,为开发者提供更强大、更灵活的 AI 应用开发工具。对于需要状态管理的复杂应用场景,还可以参考 OpenAI Responses API 的深度集成方案。
建议读者从本文提供的代码示例开始实践,逐步构建自己的 Function Calling 应用,并在实际项目中探索更多创新的应用场景。在这个 AI 技术快速发展的时代,深入理解和熟练运用 Function Calling 技术,将为你的 AI 应用开发之路提供坚实的技术基础和无限的创新空间。

